
Eat to Improve your Heart Health
Many people fear a heart attack. Think of it as the last straw. Heart disease is, in many cases, a lifestyle disease that is avoidable and, with the right focus, you can avoid it, too.
There are some pretty big risk factors (outside of smoking and drinking in excess), and these include being diabetic, having high cholesterol and being overweight. But did you know that being menopausal, having conditions such as PCOS, and being of black or Asian ethnicity can increase your chances too? And genetic predisposition can affect it too.
What I want to talk to you about today is which dietary changes you might start to make from today, to protect your health and that of your loved ones. There’s fantastic news in this regard because a number of huge studies point to diet and lifestyle change being IT when it comes to prevention.
The INTERHEART study, published in the Lancet in 2004, followed 30,000 people in 52 countries. Researchers found that lifestyle changes could prevent at least 90 percent of all heart disease.
This was another big one: the EPIC study in 2009 looked at how 23,000 people adhered to 4 simple behaviours: not smoking, exercising 3.5 hours a week, eating a healthy diet, and maintaining a healthy weight. Sticking to these four behaviours alone seemed to prevent 93% of cases of diabetes, 81% of cases of heart attacks, 50% of cases of strokes, and 36% of cases of all cancers.
A SIMPLE STRATEGY FOR GOOD HEALTH
Of course, everyone is individual, and there is no official ‘single diet’ that all humans should eat. But if there were, this would be it because it handles what the essence of the problem is – overweight and a highly inflammatory internal environment.
Before I dive in with some of the answers, I want to say a little something about fat because chances are, if you’ve heard one thing about staving off a heart attack, it’s ‘cut back on fat’ (and especially the saturated kind).
The success of some low-fat dietary models in weight loss is thought to be more likely due to the simultaneous reduction of sugar, refined carbohydrates and processed foods.
Dietary fat actually turns off fat production in your liver. Unlike carbohydrates and protein, dietary fat does not trigger your pancreas to secrete insulin.
There is one type of fat everyone should avoid, and it’s trans fats, a kind of Frankenstein fat added to food to improve shelf life and mouth-feel of products. One study actually found that the risk of coronary heart disease doubled with each 2 percent increase in calories from trans fats (Iqbal, 2014). Another researcher even concluded: “On a per-calorie basis, trans fats appear to increase the risk of CHD more than any other micronutrient.” (Mozaffarian et al., 2006).
THE REAL VILLIANS…
The real villains in the piece are refined grains and sugar. During processing, refined grains are stripped of the bran and germ, two parts of the grain kernel that contain a wealth of nutrients. The final product is starch with next to no nutritional value, providing little more than carbohydrates and calories. Refined carbohydrates can be found in a wide variety of foods, including white bread, pasta and rice, muffins, cakes, cookies, crackers, and bagels. Unfortunately, these foods make up a pretty good chunk of the modern Western diet and may be linked to a higher risk of heart disease. One study from China found that a higher carbohydrate intake, mainly from refined grains, was associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease among 117,366 adults (Yu et al., 2013).
Sugar is one of the main culprits of heart disease. Added sugars from foods like sweets, desserts, juice and soft drinks can spike blood sugar levels, damaging the blood vessels, overloading the liver and increasing the risk of heart disease.
Interestingly, a study from Harvard School of Public Health actually found that participants who drank the highest amount of sugar-sweetened beverages had a 20 percent higher relative risk of developing coronary heart disease than those who drank the lowest amount (de Koning et al., 2012).
WHAT THIS MEANS IS …
A lower carbohydrate diet is recommended to balance blood sugar and therefore reduce insulin and blood glucose levels. Elevated insulin is a major risk factor for heart disease and promotes inflammation. You’re also likely will lose weight on a blood sugar balancing diet, and that in itself will reduce the risk for many chronic diseases, including heart disease and high blood pressure.
Do you notice a trend in my diet tips? What’s to focus on is real food. What you would benefit from decreasing is the processed stuff most people kid themselves is OK for them to eat. Truly, your body doesn't know what’s going on when you shovel in heavily processed or chemically altered foods.
Eating this way - sometimes referred to as a low GL (glycaemic load) diet - will also help, providing your body with a steady supply of energy through the day, rather than a high-octane rollercoaster of energy spikes and troughs.
Putting the food work into your life alongside the commitment to regularly de-stress, move your body and prioritise sleep is not always easy to do on your own. It is always helpful to have someone – like me – in the wings helping you fit what you already know about eating well into your life and keeping you motivated to follow your plan for long enough that you really see a shift in your health.
If you would like to know more, why not book in for a free 30 minute health review here.

Increase your antioxidants
Want to bulletproof your immunity? You need to stockpile those natural antioxidants (and not just the packets and tins of pulses!). When you supercharge this “antioxidant potential” you give your immune system a real boost.
And, if you’re wondering ‘where have I heard about antioxidants before?’ they’re the things skincare companies tell you their anti-ageing moisturisers are full of so double win.
Why are antioxidants important?
Viruses and bacteria produce oxidants, which are reactive forms of oxygen that damage cells and age you faster. Simply, they are bad news. We’re also getting our fill of oxidants from eating chargrilled/ blackened foods or breathing polluted air, and maybe you’ve had a less than great diet over the years. Where you can end up is a situation in which you have too many oxidants and not enough antioxidants.
Revving up your antioxidant status at times like these is a really good idea. While vitamin C seems to get all the praise when it comes to immunity, there’s another molecule that is the under-recognised supporting actor who deserves the starring role – glutathione.
Glutathione – the master antioxidant
Glutathione is one of the most important molecules in the body – almost like a magic elixir of health. Too little of it and you’re at risk of developing one of the most feared health conditions facing us today, including stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, and heart disease.
If you’ve got good enough levels, that’s where the gold is…
But when levels are adequate or high, that’s when the magic happens. You’ll not only have protection from the conditions above, but you’ll have amazing energy, glowing skin, healthy detoxification, strong heart and brain function, and possibly even a longer life!
Glutathione is made up of three amino acids called cysteine, glycine, and glutamic acid (or glutamate). It’s often called the “master” antioxidant because it helps recycle all the other antioxidants in your body like vitamins C and E, as well as alpha lipoic acid and CoQ10.
Research show glutathione primes the white blood cells of the immune system and helps them produce more infection-fighting substances so they can control both bacterial and viral infections.
Foods to increase glutathione
Eating the right foods to naturally increase glutathione will help keep you fighting fit. There are a small number of foods that naturally contain glutathione. These include asparagus, avocado, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, spinach, broccoli, garlic, chives, tomatoes, cucumber, almonds, and walnuts.
Some other foods contain the building blocks needed to make glutathione (they are the pre-cursors – the warm-up act); the foods containing cysteine and other sulphur-containing foods, and selenium.
Good foods to choose are onions, spring onions, shallots, leeks, kale, bok choy, rocket, spring greens, watercress, radishes. Some spices such as turmeric, cinnamon and cardamom - have compounds that can also help to restore healthy levels of glutathione and its antioxidant enzymes.
Alpha Lipoic Acid – glutathione’s reloader
Alpha lipoic acid (also called ALA) is a critical co-enzyme that helps to recycle many antioxidants, including vitamin C, E and also glutathione. It is well known for its anti-ageing effects on our cell’s energy factories, the mitochondria.
Good food sources of alpha lipoic acid include:
• Organ meats
• Beef
• Brewer’s yeast
• Broccoli
• Spinach
• Brussels sprouts
• Peas
• Tomatoes
Selenium is an important trace mineral that is key in the production of glutathione (it also happens to be great for thyroid function so if yours is a little off, consider getting more of this antioxidant a double win). Good dietary sources of selenium include:
• Seafood
• Oysters
• Brazil nuts
• Eggs
• Mushrooms
• Whole grains
• Organ meats
• Dairy products
So rather than reaching for an immune supplement, why not think about how you can increase these immune-supporting foods in your diet?
Or, if you're struggling for inspiration, why don’t you book in a free 30-minute health review with me – just click here.

How useful is the BMI?
If you read magazines, watch TV, see a doctor occasionally or have ever been on a diet, you’ll have heard of the BMI or body mass index. It is a number used to assess whether a person is underweight (BMI <18.5), of a healthy weight (18.5-24.5), overweight (25-30) or obese (>30). It is calculated by dividing body weight (in kilograms) by height (in metres) squared.
Although widely used and known by all, the BMI is not actually a very useful parameter to assess health or even weight. Why?
Take a chunky rugby player, six feet (183 cm) tall, weighing 16st (101kg). His BMI is 30.3, making him ‘overweight’. Yet he has a 32-inch waist, is all muscle and fighting fit. Now compare him to an armchair rugby watcher, also six feet tall, weighing 16st, but with a beer belly and a largely sedentary lifestyle. He would have the same BMI, but it doesn’t take an expert to see that the two men couldn’t be more different. For this reason, the BMI alone has limited significance in assessing good health because being ‘overweight’ or not according to BMI means nothing without knowing one’s body composition.
The BMI does not account for a person's muscle mass. In very muscular people, it suggests ‘overweight’ when they really are slim and healthy. In older people, a ‘healthy weight’ can be anything but, because muscle mass decreases with age, and their fat percentage is high for their weight. In addition, the BMI categories used in Western countries are less suitable for people of other ethnic backgrounds because they have a different stature than white people.
What is body composition, and why does it matter?
'Body composition' is the body's ratio of water, muscle, bones, and fat. A body fat percentage of 8-25% is considered normal for men and 20-35% for women. Knowing where the body fat is situated also gives clues about our health. Studies have shown that fat deposited in the abdomen is more problematic than fat elsewhere because it is metabolically active, upsetting hormone levels and causing or exacerbating inflammation. It can also surround and even penetrate vital organs, impairing their function.
Muscle mass, on the other hand, is ‘expensive’ tissue. That means it burns more calories than fat. The basal metabolic rate (BMR) describes the minimum number of calories a body needs to function. Most people’s BMR lies between 1,000 and 2,000 kcal/day, depending on height, weight, sex, and age. If that strikes you as too little, you’d be right. This is just the absolute minimum of calories you need to lie down and breathe. Once you consider activity levels, the calorie requirement goes right up. A low BMR means your body doesn’t burn many calories in a rested state, and you are likely to put on weight quickly, finding it hard to shed. Building muscle increases the BMR because even when not in use, muscle tissue requires energy, i. e. it burns calories.
How can I measure my body composition?
Accurate body composition often reveals surprises. People with a favourable BMI may turn out to be TOFI: thin on the outside, fat on the inside.
Elaborate methods are used in research to determine body fat percentage as accurately as possible. In a medical or nutritional practice, a so-called bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) can help to estimate the body fat percentage. It also usually calculates the BMR. BIA devices measure the resistance in the body and thereby evaluate the body’s water content. From this, in turn, the fat content can be roughly estimated. However, it is not necessary for most people to determine the exact body fat percentage. There are also commercially available scales that make it possible to estimate the body fat content using BIA.
Another measurement you can use is the waist-to-hip ratio. It is calculated by dividing the waist circumference in centimetres by the hip circumference in centimetres. A value of more than 1 for men or more than 0.85 for women is considered unfavourable.
Your body fat percentage is high. Now what?
Now that you know, you can do something about it. If your BMI is high, your doctor may already have advised you to lose weight. It may surprise you that cutting calories is not the answer.
If your body fat percentage is elevated, your BMR will likely be low. Many calories you eat are not burned, and any excess is deposited as – you guessed it – more fat. Eating less (fewer calories) seems to be the reasonable solution, but the body is not stupid. If less energy comes in, it will reduce energy expenditure (i. e. reduce its basal metabolic rate). You may feel cold and tired as a result. Muscle tissue may be burned for energy, with the added bonus that it is then gone and won’t cost the body any more of those precious calories. After a while, you’ll get fed up with being tired, cold and hungry all the time and start eating more again. But – surprise – you put any weight lost back on and then some because now that your body has turned down the dial, you are burning calories even less efficiently than you did to begin with. From now on, you are likely to put weight on even more quickly than before.
Increasing the BMR, however, is a lot more helpful; for this, you need to build muscle. More calories need to be burned to supply all this new muscle tissue with energy, and less gets deposited as fat. In fact, if you play your cards right, that pesky body fat can even be burned for energy. Your body composition improves as muscle tissue builds up and fatty tissue is reduced.
So, to improve your body composition, you must find a way to
Here are my tips to improve your body composition.
Low-carb eating for fat loss
Decreasing your intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates can have a beneficial effect on body composition. Numerous studies report improved body composition with a low-carb diet.
Every time we eat, our blood sugar - or rather blood glucose - level goes up. Whether that's by a little or a lot depends on what the meal consisted of. If it was high in sugar or refined carbohydrates, the blood sugar level rises high. If it was a meal with few carbohydrates and most of those complex carbs, it might just go up a little.
High blood sugar is hugely damaging to body cells. It ‘sugar coats’ cells, making them stiff and unresponsive. As that can be almost any kind of cell, the symptoms caused by long-term high blood sugar (aka diabetes) are highly varied and can affect the heart, the kidneys, the eyes, the nerves incl. the brain, and more. To avoid damage, if blood sugar (glucose) levels are high, insulin is released to bring them back down to a healthy level again as fast as possible.
Insulin works by moving glucose inside cells, where it can be used to create energy. However, the cells can only take up so much glucose at any given time. What can’t be squeezed in will continue to circulate, and that’s not an option. So, another thing insulin does is convert excess glucose into fat, which gets stored in fat cells. It can be converted back into glucose if needed, though it usually never is. Instead, more and more glucose from sugary and starchy foods adds to the build-up of fat every day.
Foods that are low in carbs but high in fat and/or protein do not have that effect. Yes, even fat does not make you as fat as sugar and carbs! The food we put into our mouths is more than the sum of its components. What really matters is what our metabolism makes of what we supply. Therefore, it is not as simple as: “Fat makes you fat”, no matter how logical that sounds.
If glucose levels rise fast and high (as they do after sugary or starchy foods), a lot of insulin is released at a time to deal with the problem as quickly and efficiently as possible. As a result, the blood sugar level drops again, now overshooting its mark and ending up too low. This, too, is a problem, as a certain amount of glucose is required at all times, not least to support the brain. At this point, you may feel tired, unable to concentrate, irritable and hungry. Willpower and reason go out of the window. We now need something fast, ideally something sweet as we know it will make us feel better.
Fatty foods do not affect blood sugar levels at all, and high-protein foods only minimally. Complex carbohydrates – the kind that releases glucose slowly – raise blood sugar levels gently and not as high. Less insulin is required to deal with it, and that, in turn, reduces blood sugar drops, too. You’re fuller for longer, and cravings become a thing of the past.
Eat protein with every meal
Making sure that good quality protein is part of every meal you eat kills two birds with one stone. Because it barely affects blood glucose, there will be no steep drops, and you’ll not end up as ravenous as you would on the usual high-carb diet. Being hungry all the time is what makes most people fall off the waggon when dieting, so, clearly, avoiding hunger is a significant advantage.
To improve your body composition, you’ll also need to build muscle. You'll exercise to achieve that, but that new muscle must be made from something, which is where protein comes in. To create new muscle tissue, you need protein, so tuck in!
Good protein sources are meat, fish, seafood, eggs and dairy. The best vegan ones are nuts, seeds and pulses (beans, lentils, chickpeas – also contain carbs). However, they are not 'complete', meaning they do not have all eight essential amino acids. The way around it is to also include grains in the diet – which are, of course, a source of starch. Grains and pulses don’t necessarily have to be consumed in the same meal, but both must be part of a vegan diet.
Sustainable calorie reduction
On the face of it, this seems to be the trickiest part. We have seen, after all, that eating too little only causes the body to reduce the basal metabolic rate, which is counterproductive, so we must find a way to preserve muscle despite a low calorie intake. Also, we know that low-calorie diets make us miserable, making it less likely for us to continue.
One gram of fat contains 9 kcal. The same amount of carbohydrate or protein contains just 4 kcal. It looks like a no-brainer: Cutting out fat will hugely reduce the calorie intake, and it is for that reason that conventional diets recommend you do that. Yet, as we have seen, metabolic processes matter much more than the actual number of calories. Low-fat inevitably means high-carb, and we’re en route to weight gain and misery (see above). As protein is just as low in calories as carbohydrates, I recommend increasing the share of protein in your diet.
How filling are starchy carbs? Does a bag of crisps or a packet of biscuits stave off hunger? Most people’s experience is that not long after eating starchy carbs, hunger starts niggling again and – surprise – there seems to be room for more. Not so if you increase your protein intake. You’ll soon find that you’re satisfied. There is only so much protein you can eat. That way, diets that are higher in protein naturally reduce calorie intake.
Time-restricted eating
Another way to effortlessly reduce calories is time-restricted eating. This means eating only during an 8- or 10-hour window and not eating during the remaining 16 or 14 hours of the day. That means just skipping one meal – either breakfast or dinner – and not snacking during the fasting period.
This way of eating may be much closer to the eating pattern we evolved to maintain. Hunter-gatherers don’t usually sit down for breakfast, lunch and dinner, after all, snacking in between. Humans evolved to eat when hungry and could only eat when the hunt or the foraging trip had been successful. Our bodies are well equipped to bridge the gap while we’re not eating. Body fat accumulated when food was available can now be converted back into glucose. This process cannot happen when glucose levels are up all the time. During fasting, with no new energy coming in, there is finally an opportunity to burn fat.
Not eating for 14 to 16 hours every day may seem daunting. You may find time-restricted eating difficult if your diet is based on carbohydrates. However, if you increase your protein intake and consume adequate healthy fat, you may be surprised to find that you are not feeling hungry and do not even miss that meal you’re skipping.
What not to eat or drink
If you want to improve your body composition, there are certain foods or drinks you may want to give a wide berth:
Cakes, biscuits, crisps, ice cream, ready meals, takeaways and almost anything you can buy ready to eat is not just highly processed but also choc-full of unhealthy fats, sugar, salt and additives. These foods are designed to make us want more. It's not your fault that your hand repeatedly goes back into the crisp packet until it’s empty. You’re supposed to. The best thing you can do for your body is to learn how to prepare your own meals and snacks from scratch. They’re tastier, healthier and more satisfying.
Soft drinks are sugar dissolved in water. Regarding our metabolism, it does not even make a difference whether your drink is cola or freshly squeezed fruit juice. The latter may contain more nutrients than the former, but the sugar content is almost exactly the same, and so is its impact on your blood sugar levels. If you regularly consume soft drinks, switching to water is the single most significant step to improving body composition.
Like soft drinks, alcoholic drinks contain just empty calories. They do not have any nutritional value and are even toxic. Avoid.
Improve your body composition
So, there you have it. The BMI is a less than useful measure of body weight. What really matters is body composition. If you need to lose fat and build muscle, implement the dietary changes described above and introduce regular resistance exercise into your life.
Want to know more? Why not book in a free 30 minute health review with me – just click here.
Increase protein and keep your carb intake low. Low-carb diets are much better at promoting fat loss than low-calorie diets. At the same time, they are more sustainable as you won’t feel as hungry. Once you get settled into your low-carb diet, up the ante by introducing time-restricted eating. However, take care not to restrict your calorie intake too much as this may cause the loss of muscle mass.
Want to know more? Why not book in a free 30 minute health review with me – just click here.

The link between physical health and what you eat is well understood, but did you know that what you eat has a huge impact on your mood and how you feel?
I wonder how we forgot about this connection, because it was common knowledge in times gone by. Way back when (think medieval times), people would eat quince, dates and elderflowers if they were feeling a little blue, and use lettuce and chicory as nature’s tranquilisers.
Modern science has extensively studied the impact of food on mood, and we now understand why food has such a positive (or negative) effect, and also which foods we should be eating more (or less) of to support mental health.
Managing anxiety, stress, depression, and other mood disorders is complex, and there’s no one-size-fits all solution. But we know that the right diet and lifestyle plan combined with motivational coaching to help you every step of the way can be an enormous help.
Good nutrition makes all the difference
The very edited highlight of the research into what you should eat to balance your energy and improve your mood is to follow a Mediterranean-style diet featuring plenty of whole, natural foods. That also means learning to balance your blood sugar levels. Loss of blood sugar balance has a clear link to stress, anxiety, and depression. 50% of low mood is down to blood sugar imbalances.
Learning how to become a master of your blood sugar balance is the secret to having more energy, a better mood and controlling your weight – and losing it if you need to. Feeling more confident about the way you look is in itself an excellent way to boost feelings of self-worth.
In the same way that eating well can positively influence mood, making poor food choices can have the opposite effect. Research by a team at Binghamton, New York, showed that young adults under 30 who ate fast food more than three times a week scored higher when it came to levels of mental distress. The same researchers found that those who ate meat fewer than three times a week had more mental health problems (potentially as the amino acid tryptophan found in meat is the pre-cursor to the feel-good chemical serotonin).
Key to your mood and brain function
Few of us get enough omega-3 fats in our diet, and these are key to our mood and brain function. The dry weight of our brain is literally 60% fat - so not surprising that we depend on a daily intake of essential fats.
EPA, DPA and DHA – certain long-chain omega-3 fats – build and rebuild your brain and are part of the equation for happiness. The higher your blood levels of omega-3 fats, the higher your levels of the feel-good neurotransmitter serotonin are likely to be.
Omega-3 fats help build receptor sites as well as improving their function. There have been ten good quality double-blind controlled trials to date, giving fish oils rich in omega-3s to people with depression. Five showed significant improvement, greater than that reported for anti-depressant drugs.
Most studies on anti-depressant drugs report something like a 15% reduction in depression ratings. Three studies on omega-3s reported an average reduction of 50% - and without side-effects.
Sources of omega-3 fats: oily fish (salmon, trout, mackerel, sardines, cod, tuna, halibut), walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseed. If you are vegetarian or vegan, consider taking an omega-3 supplement (e.g. DHA from seaweed). Most plant sources of omega-3 do not contain the long-chain fatty acids mentioned above. Although the body can make those from short-chain omega-3s – like the ones found in nuts and seeds – conversion is poor and it is difficult to get enough omega-3 that way, especially if you are not in good health or pregnant, when you need some extra.
Low mood affects up to 20% of us at any one time
Low mood affects up to 20% of us at any one time, so everyone is likely to experience some form of it at one time or another, particularly if you are also tackling a gut or hormone issue.
Many periods of low mood can be almost eradicated by following the simple steps above and by following my signature Mood & Energy programme. Not only because this addresses many of the physical causes of low mood, but also because you are spending your time focusing on a positive action plan and learning new things rather than ruminating about problems.
To find out more about how a nutrition & lifestyle programme can help, click here to book a free call with me.
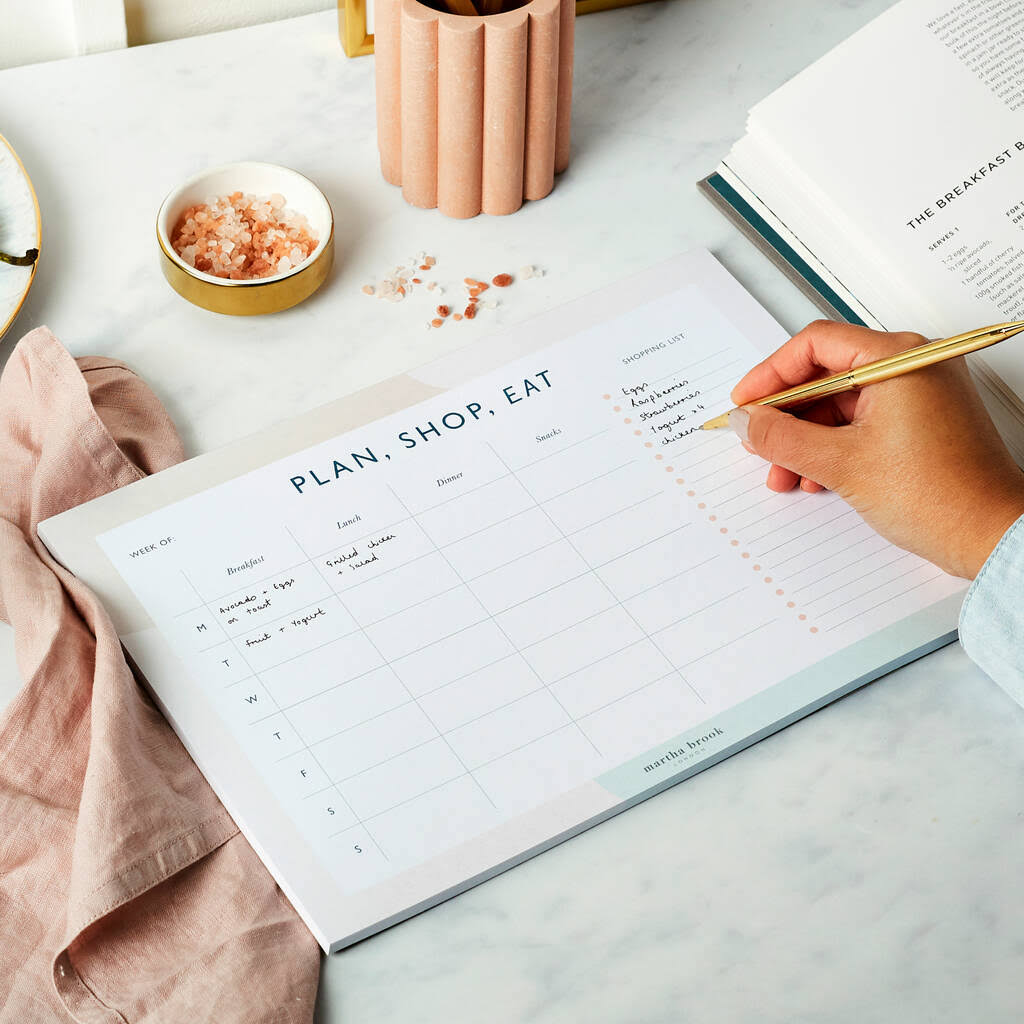
Plan for the life you want to create
How often have you started following a healthy eating plan only to be forced to make unhealthy choices because you didn’t have the right foods in the fridge, you didn’t have time to eat a ‘proper’ breakfast or make the lunch you wanted to take to work? I’m guessing quite a few because that’s just what happens when life gets in the way.
You’ve probably heard the saying ‘failing to plan is planning to fail’. Or maybe ‘goals without a plan are just wishes’? They are things that we want but we have not yet committed to doing them…
Without a weekly food plan, it will be pure luck if you end up with the right foods in the fridge or cupboards. And, without planning your time, you won’t always make the time to enjoy breakfast or make that lunch.
Here’s the thing about planning:
It’s easy to get derailed by events, situations, relationships, and tasks that insert themselves into our already-busy lives. So, if you’re committed to changing the way you eat, losing weight and, in fact, making any change in your life, this post is perfect for you.
The very first thing you need to do is to find time to sit down and plan your meals. When can you do that? Get that in the diary now.
If you’re one of those super-busy people who always finds themselves complaining that they don’t have time, I have an exercise for that, too. You see, ‘not having time’ is a story we tell ourselves or other people in order not to have to take responsibility for – or actually have to do – a particular thing. Sorry to be the one to break it to you, but you make time for what you prioritise in life. Anything else is just an excuse.
If you’re reading this thinking, ‘yes but…’ let’s take a look at how you are spending your time.
Ask yourself how you feel about how you are spending your time. Are you in control of your time? If you looked back over your life, would you be happy with the way you had spent your time?
Every day over the next week use a daily planner to jot down everything you are doing in the time slots provided. This can help you discover the REAL reason behind what you say you want and what you actually do. It’s common, for example, to realise you are spending 15##plus## hours a week randomly online (on Facebook, following links or doing ‘research’).
Where you are losing time or being inefficient with it? What is the cost to you of spending your time like this?
Does it make it impossible to follow a healthy eating plan? Are the Starbucks breakfast bills piling up because you haven’t made time to get breakfast at home? How is this working for you? It’s often incredible how much time you gain so reorganise your life in a new way to fit in your new healthy habits.
Organise your week
Once you at the set-aside time in your diary when you are going to plan your meals, work out when you are going to fit in the shopping. Can you allocate time to go to the supermarket? Or can you book in an online grocery delivery. Get that in the diary now too and book the slot.
Next, work out what’s happening over the course of the week. Are you going out to eat any days? Do your kids have after-school clubs or packed lunches that need making? Are you working late one evening, so might need a quick fix supper? With these in mind, mark in your journal which meals will fit with which occasion.
Then check your cupboards and fridge for ingredients you may already have for these meals, so that you don’t double up. Write up a shopping list for the ingredients you need for you to take to the supermarket, or put these items into your online shopping basket.
Job done!
You now have a week’s worth of meals planned, ingredients organised, and shopping on its way. You can rest assured that you are eating well and won’t be tempted to order a takeaway as you don’t have the rights foods in! Plus, you know that there isn’t going to be a whole heap of food waste going on, so it’s better for the environment too. It’s a win-win!
And if you’d like some help coming up with a weekly menu, drop me a line! I’m here to help people plan what works for them and their families.

How do you reward yourself? How do you comfort yourself when you are stressed? Think about that for a moment.
Rewarding yourself for your successes, both large and small, is a key part of staying motivated.
We are so time poor that rewarding ourselves with treat foods like cake and biscuits is the easiest way to show ourselves some self-love. And it’s the same for soothing ourselves if we’ve had a bad day.
My experience of running a nutrition clinic is that so little of what or why people eat has to do with nourishing their body. The far greater part is to do with how you feel about yourself and about life in general. Eating half a packet of chocolate biscuits is much easier than figuring out – not to mention getting – what you really need, which might be a way to de-stress, feel loved, get attention, kick back your heels and even sleep. Many people are almost completely out of touch with their own bodies.
When I’m working with clients, one of the big things we are trying to achieve is to develop a different relationship with food and, also, a different relationship with rewards.
Building in ways of making yourself feel good are essential for a number of reasons. Perhaps the biggest among them is that you need to positively reinforce the fantastic healthy changes you are making to encourage you to maintain them long term.
You need to build in more appropriate ways of making yourself feel better: far better to automatically choose to spend five minutes relaxing in the sunshine in the garden to recharge your batteries than to grab a handful of biscuits.
Most of our rewards are habit. They are conditioning. Chances are, you have been conditioned to reward yourself with food, often from early childhood.
Normal ‘rewards’ are short lived and usually followed by recriminations. If you truly want lasting change, you need to find ways of regularly getting that feel-good feeling from other things. You’ll want to build in more appropriate ways of making yourself feel better and look forward to non-food related treats.
I encourage my clients to build up a list of non-food treats to avoid any feelings of deprivation. After a while, you will prefer these rewards and benefit from them far more than food treats that simply create other problems for you later.
Regular ‘me time’ is important here as our lives are very busy and many of us have got into the habit of relying on food to give us a quick pleasure fix. But, as we know, this ‘reward’ is short lived and usually followed by disappointment plus a large serving of guilt! If you truly want lasting change, you need to find ways of regularly getting that feel good feeling from other things. We all deserve and need time to do positive things for ourselves - without feelings of guilt.
Improving our relationship with food is all about changing behaviours. We know that the carrot is more effective than the stick for long-term, self-motivated change. So, as well as deciding on your big rewards for achieving long term goals, think of a few quick and easy things you can do at least 3 times every week.
So, as an example, you might be better to CHOOSE to spend 5 minutes relaxing in the sunshine in the garden to recharge your batteries than to grab a handful of biscuits.
It can be a really empowering exercise to take a look at what you might normally do to reward yourself and think, are these appropriate now or do I need to replace them.
Most of the time it’s a simple as putting in a new habit to replace the old one. And, even better when the new habit is one that you really enjoy! All this is good for your physical and mental health.
Spend some time to identify some activities that you can build into your daily life that you enjoy and can use as your reward / destressor / way of taking a break / or just to have 5 minutes of indulgence or peace!
What would you like to spend more time doing? What would make you feel good?
What would help you relax or de-stress?
A few examples:
Add your own: think of at least 5 things that relax you...
Bored vs reward?
Most people can identify with eating when they were really bored. This often leads to mindless eating just to experience that sugar rush to give you a temporary high. Or it may simply be that you need something to occupy your mind and hands as a distraction technique. If you recognise yourself doing these things, then this is a great opportunity for you. It actually means that you are looking for something fun / exciting / interesting to add into your life. Use this as an opportunity to improve the quality of your life and build in new ways of enjoying yourself and enriching your experience of life.
Simple steps to better rewards
What are your personal interests? What activities do you enjoy?
What do you enjoy? What would you like to try? If you know this is something you want to improve on, it's worth spending a little time writing a list (in a notepad or on a phone rather than keeping it conceptually in your head). Choose one and have it as one of your goals for this week.
And if you’d like some help, why not book in a call with me here?
![]()
Please get in touch and find out more - I offer a free 30-minute exploratory call.